What is land drainage for?
Land Drainage in Agriculture
Efficient drainage in agriculture is essential to maintaining a good ground surface. Loss of use due to water logging or turf damage can be eliminated by land drainage, and an improved drainage system can improve soil structure and provide better quality vegetation and grass.
Land Drainage in Construction
In construction, it's important to remove surface water from the ground surrounding a building to prevent flooding. Ground water can also increase static load on underground structures and retaining walls, and land drainage can be used to relieve this pressure.
Types of Land Drainage
Land drainage products from JDP are available in coiled sizes 60mm to 160mm, from 25m to 150m in length. There are two main types of land drain: perforated and unperforated.
Perforated Land Drainage
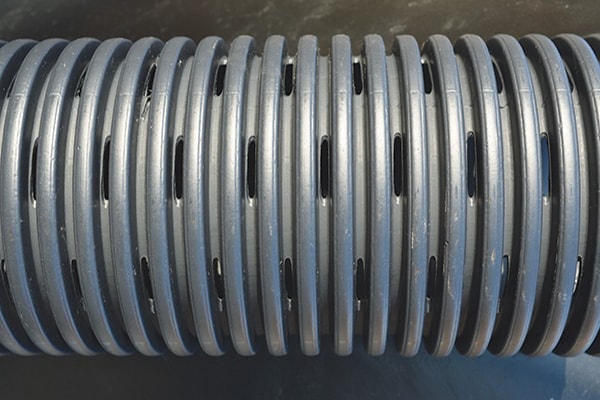
Also called filter drain or slot drain; this pipework has small holes cut inside the corrugations of the pipework that allow water to drain into the pipe.
Unperforated Land Drainage
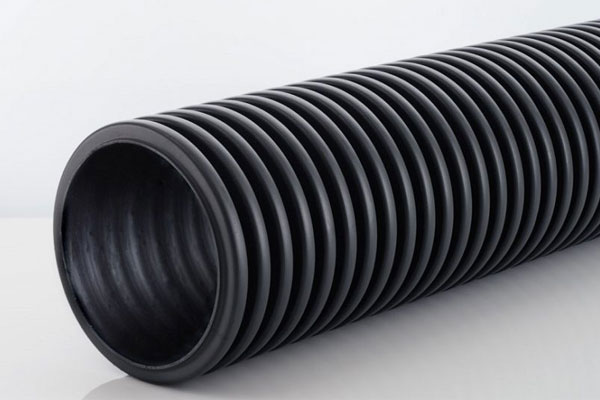

Also called carrier drain; this pipework is solid and has no holes in its corrugations. Used to carry (and not collect) water to a designated discharge point.
Perforated Land Drainage
| Pipe Diameter (mm) | Coil Length (m) | Code |
|---|---|---|
| 60 | 25 | 0504SP6025 |
| 60 | 50 | 0504SP6050 |
| 60 | 150 | 0504SP60150 |
| 80 | 25 | 0504SP8025 |
| 80 | 50 | 0504SP8050 |
| 80 | 100 | 0504SP80100 |
| 100 | 25 | 0504SP10025 |
| 100 | 50 | 0504SP10050 |
| 100 | 100 | 0504SP100100 |
| 160 | 45 | 0504SP16045 |
| 160 | 50 | 0504SP16050 |
Unperforated Land Drainage
| Pipe Diameter (mm) | Coil Length (m) | Code |
|---|---|---|
| 60 | 150 | 0504SU60150 |
| 80 | 50 | 0504SU8050 |
| 80 | 100 | 0504SU80100 |
| 100 | 25 | 0504SU10025 |
| 100 | 50 | 0504SU10050 |
| 100 | 100 | 0504SU100100 |
| 160 | 45 | 0504SU16045 |
| 160 | 50 | 0504SU16050 |
Land Drainage Installation
Drainage plans should clearly show the location of the drain runs, spacings, levels and other relevant information necessary for the correct installation. The minimum depth of cover on any piped drain should be at least 450mm to protect the pipe from damage due to surface traffic or maintenance operations such as deep spiking.
Inspection chambers and silt traps should be incorporated into the scheme to allow for inspection and maintenance. Consideration should be given as to whether the soil arisings from the works are to remain on site or be removed.
The choice of permeable backfill is imperative to the long-term success of the drainage scheme as, by definition, it allows passage of water from the surface to the pipe. All backfill material placed over drains should be durable, evenly graded and free from pollutants.
All drainage outfalls into watercourses should incorporate suitable headwalls fitted with a vermin guard.
