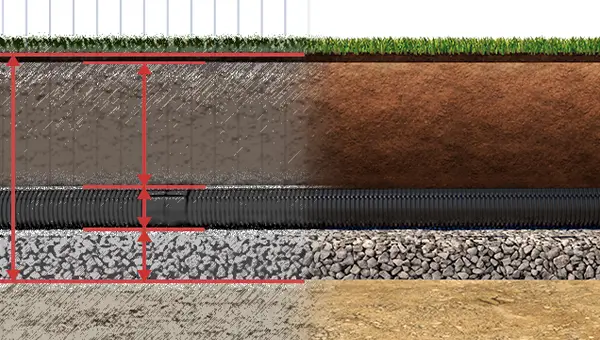
Installing a twinwall drainage system is an unobtrusive but efficient way of removing water from a surface which is being bogged down by rainwater.
But where exactly can it be installed, and what are the steps involved? These are the questions that we aim to address in this quick guide. For more detailed information, please have a read of our "Basic Guide to Twinwall" article and our comprehensive step-by-step Twinwall installation guide.
Where can I install twinwall?
Twinwall can be used for a variety of applications due to the range of size options and the choice of either perforated or unperforated pipe. The trick is in knowing how to choose the most suitable type of twinwall for your project.
It can be tempting to assume the old adage of “bigger is better” when selecting a size, believing that the larger the diameter of the pipe, the more effective it will be at draining excess water. However, while this might be true in some applications, in others, it could be too effective and actually over-dry the ground, which isn’t helpful for agricultural areas, for example.
For field drainage, where you would use twinwall to remove the surface water, you would tend to use the smaller diameters of 110-300mm in order to drain the water at a rate that doesn’t dry out the ground. Whereas for roads and highways drainage, another major use of twinwall where the surface water needs draining as quickly as possible, you would want to use a larger size, potentially up to 600mm.
To help guide you towards the right size twinwall for your project, we’ve created the following list of the most common twinwall applications and matched them with the recommended pipe diameters for each.
Typical Twinwall Applications
Please note: These are general recommendations only, and the optimal Twinwall pipe size will depend on specific project factors like water flow volume, soil conditions, and local building regulations. Consulting with a drainage professional is always recommended to determine the most appropriate pipe size for your particular needs.

Garden & Patio Drainage
Twinwall Use:
- Channelling water away from flowerbeds, lawns, patios and walkways to prevent waterlogging and damage.
Recommended Twinwall Size:
- Typically, 110mm pipes are sufficient for targeted drainage in gardens and patios.
- In some cases, 150mm pipes might be recommended for larger areas or heavier water flow.

Driveway Drainage
Twinwall Use:
- Ensuring proper water flow and preventing puddles from forming.
- Particularly useful for large gravel driveways. (Want to know more about drainage in gravel driveways? Take a look at our Driveway drainage article).
Recommended Twinwall Size:
- 150mm pipes are generally suitable for standard driveways.
- For larger driveways or heavy traffic areas, 225mm pipes might be a better option.

Building & Construction Drainage
Twinwall Use:
- Channelling away groundwater to protect foundations.
- Safeguard utility cables and pipes from water damage.
Recommended Twinwall Size:
- 225mm pipes are commonly used for foundation drainage and utility protection.
- Larger projects or high-water table areas might require 300mm or even 375mm pipes.

Roads & Highways Drainage
Twinwall Use:
- Efficiently managing water flow to prevent road damage and minimise disruptions to traffic.
Recommended Twinwall Size:
- 300mm pipes are often used for highway shoulder drainage.
- Major highways with high traffic volume might require 375mm or even 400mm pipes.
- Up to 600mm for major motorways or complex drainage systems.*

Agricultural Drainage
Twinwall Use:
- Maintaining optimal soil conditions for healthy crops by preventing waterlogging.
Recommended Twinwall Size:
- 150mm pipes are typically suitable for smaller fields or sub-surface drainage systems.
- 225mm or 300mm pipes are best for larger fields or deeper drainage needs.
- Extensive agricultural operations might require up to 400mm pipes for efficient water flow management across extensive fields.*
*always consult a professional for larger diameter applications.
Twinwall pipes can also be used for sports fields, retaining walls, golf courses, and more. Take a look at our “Unconventional uses for our pipes”“Unconventional uses for our pipes” case study to see some of the more unusual and innovative ways twinwall can be used.
How do I install twinwall?
Twinwall is installed using a trench method, which is completed by sidefilling/backfilling. Below is a quick overview of the recommended installation process for a domestic twinwall application.
Note: Twinwall should always be installed in accordance with the manufacturer’s guidelines.
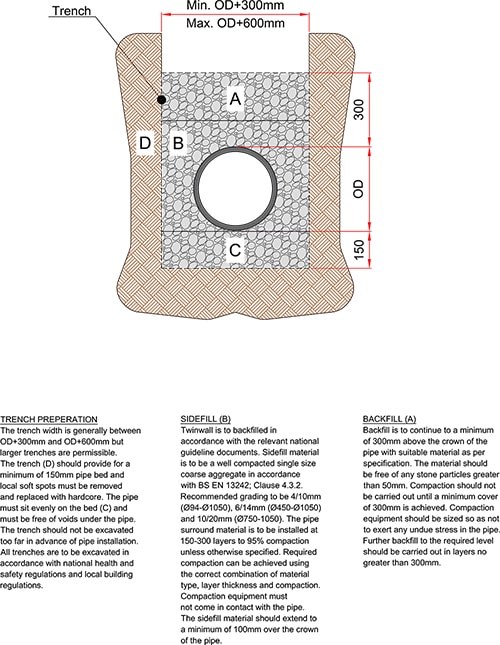
Step 1. Prepare the Trench
The trench that you dig should have a pipe bed upon which the pipe should sit evenly, and it must be excavated in accordance with health and safety regulations.
- The width of the trench is normally between 410mm and 1200mm. However, larger trenches are acceptable, especially for perforated systems.
- The depth of the trench should allow for 150mm of gravel below the pipe, the height of the pipe, a 300mm layer of gravel above the pipe, and then the thickness of the surface layer that needs to be restored after the installation is complete.
For more advice about the recommended depths and widths for specific pipe diameters, have a read of our “How to plan a Twinwall Drainage System Installation” article.
Step 2. Add Pipe Bedding
Fill the bottom of the trench with 150mm of gravel—we recommend small, well-granulated gravel that must fully support the pipe.
Step 3. Lay the Twinwall Pipe
Install the twinwall pipe on top of the bedding, utilising any couplers, bends and junctions that might be needed to achieve the desired system layout.
Step 4. Sidefilling around the Pipe
Again, we would recommend using a small, well-granulated gravel to fill the space on either side of the pipe to help hold it in place.
Step 5. Backfilling
The trench should then be backfilled with similar gravel, with stones no bigger than 50mm, and compacted once a cover of 300mm is achieved.
Step 6. Cover the Trench
Finally, the trench can be recovered with a suitable surface material.
And that’s it, in a nutshell. If, however, you need more information about choosing or installing Twinwall, we have a whole series of other Twinwall Drainage articles available to help. Alternatively, you can contact our team of experts, who are always on hand to help with all of your civils and drainage needs.